- Home
- Blog Center
- Project Portfolio Management Basics: Project Risk Management
Project Portfolio Management Basics: Project Risk Management
There are several actions you can undertake in order to decrease your average project completion time:
- Sequence projects within a portfolio to prioritize them based on strategy, budget, and resources.
- Plan your project and view dependencies
- Ensure the right resources with the right skills are working at the maximum utilization rate achievable.
- Implement a collaborative work management system to accelerate value-added tasks like change and issue management.
- Get reliable, consolidated data to monitor your projects’ health and dependencies and expedite decision-making.
But you should also implement project portfolio management basics like project risk management in order to minimize, manage, monitor, and control the probability or impact of unfortunate events.
Project Risk Management is a continuous process that begins during a project’s planning phase and ends once the project is successfully commissioned and turned over to operations.
Project Portfolio Management Basics: What is Risk?
As defined in A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide – Third Edition), project risk is an uncertain event or condition that, if it occurs, has a positive or a negative effect on at least on project objective, such as time, cost, scope, or quality. A risk has one or more causes and, if it occurs, one or more impacts.
What is Project Risk Management?
As defined in PMBOK® Guide, Project Risk Management includes processes concerned with conducting risk management planning, identification, analysis, responses, monitoring and control on a project.
Project Risk Management made easy with a PPM software
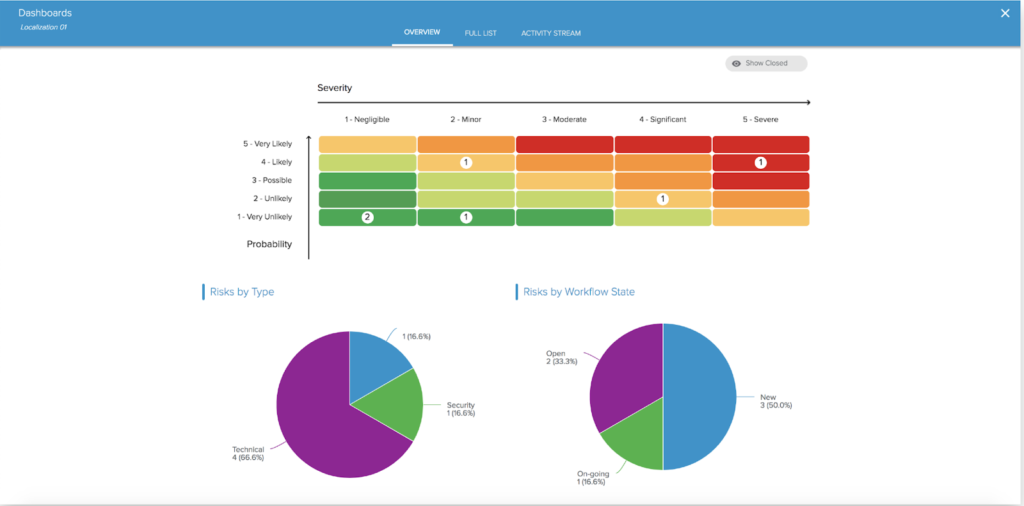
A PPM platform like Sciforma makes it easy to:
Identify risks
During the Identification phase and based on previous project experiences, Project Managers will compile a list of risks.
Analyze and prioritize risks
The Risk Analysis phase determines the likelihood of the occurrence and impact of each identified risk and prioritizes all the risks for management to review. Using the Probability and the Severity, project leaders can then rank the Risks and define their position in the Severity/Probability Matrix.
Mitigate risks
During this phase, the Project Manager assesses the project’s highest-ranked risks and defines and executes a plan to alleviate them using specific risk controls.
Run contingency plans
Although the Risk Mitigation Plan aims to decrease risk exposure, risks can still materialize. When they do, Project Managers need to come up with a Risk Contingency Plan in order to handle them appropriately.
Monitor & control risks
This phase should be set up to track potential risks, oversee the implementation of risk plans, and evaluate the effectiveness of Risk management procedures.





